Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) is a life-threatening medical emergency where the heart unexpectedly stops beating due to an electrical malfunction. When Sudden Cardiac Arrest occurs, blood flow to the brain and vital organs stops within seconds, making immediate action crucial. This condition is different from a heart attack, which is caused by blocked arteries rather than electrical failure. Understanding SCA helps people recognize symptoms early and respond quickly to save lives.
Symptoms of Sudden Cardiac Arrest
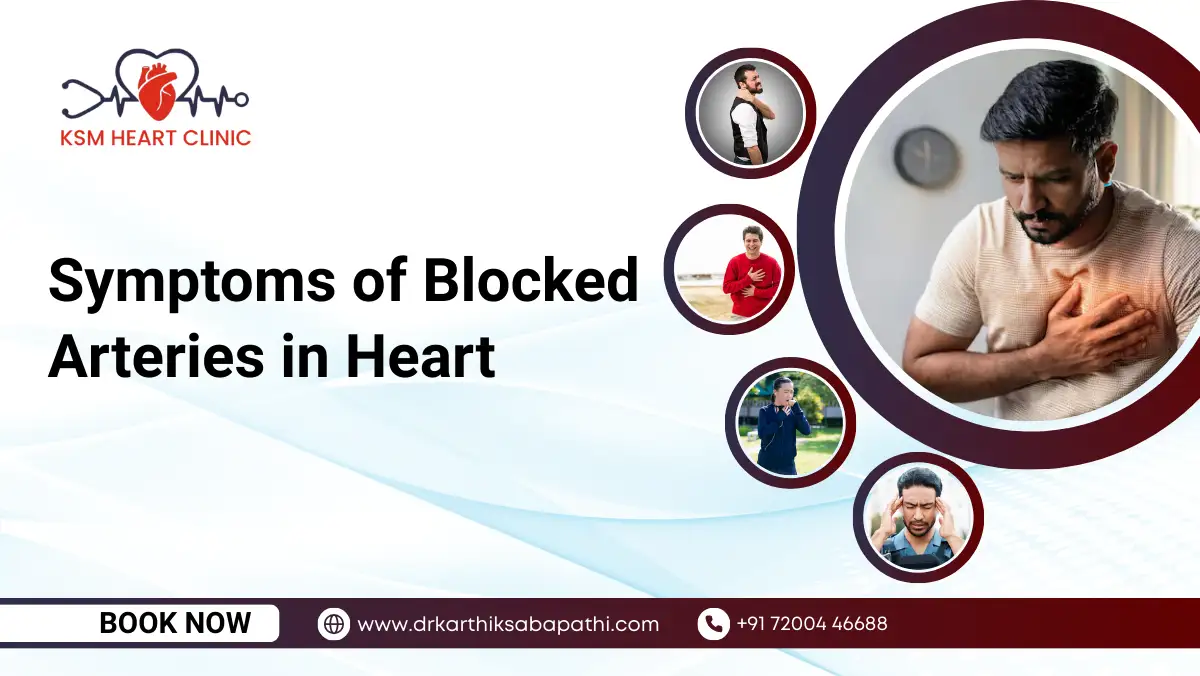
Recognizing the symptoms of this critical heart emergency is essential because it often occurs without warning. These signs help identify the underlying cause of the condition and make early detection potentially life-saving. At the same time, understanding the Signs of a Healthy Heart can help you stay aware of your overall cardiac wellness and prevent future risks.
Key Symptoms
- Sudden collapse with no response when called or shaken.
- No pulse or extremely weak pulse that disappears rapidly.
- No breathing or abnormal gasping that indicates the body is struggling for oxygen.
- Loss of consciousness within seconds due to halted blood flow.
- Chest discomfort or dizziness moments before collapse in some cases.
What Causes Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA)?
Understanding the triggers of this emergency helps reduce risks and identify individuals who may require urgent medical attention. This condition can affect anyone, but certain health issues and lifestyle factors significantly increase the likelihood of it occurring. These underlying factors are often considered the primary causes of this life-threatening event.
Major Causes Abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) such as ventricular fibrillation — the most common trigger of Sudden Cardiac Arrest.
- Coronary artery disease, where blocked arteries reduce oxygen supply to the heart.
- Heart attack, which can damage heart muscle and spark electrical instability leading to Sudden Cardiac Arrest.
- Cardiomyopathy, where the heart becomes enlarged or weakened.
- Congenital heart disorders, especially in younger individuals.
- Severe electrolyte imbalances, such as extremely low potassium or magnesium.
- Drug overdose or severe trauma, disrupting the heart’s electrical activity.
How Sudden Cardiac Arrest Differs from a Heart Attack
Although the terms are often confused, they describe two different medical emergencies. One is primarily an electrical problem, while a heart attack involves blocked blood flow. Knowing the difference helps identify the symptoms of this heart emergency accurately.
Key Differences
- Heart attack occurs when blood flow to part of the heart is blocked; the heart usually continues beating.
- Sudden Cardiac Arrest happens when the heart suddenly stops due to electrical failure.
- A heart attack may cause SCA, but SCA often occurs without any prior symptoms.
- During a heart attack, a person may experience chest pain; during Sudden Cardiac Arrest, they collapse and lose consciousness instantly.
When to See a Doctor
Timely medical attention is vital, especially for people at risk of Sudden Cardiac Arrest. Early evaluation can identify hidden heart problems and reduce the risk of life-threatening events. If you understand the reason for Sudden Cardiac Arrest, you can better decide when to seek care.
- Unexplained fainting or dizziness, especially during physical activity.
- Family history of SCA, arrhythmias, or sudden death.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat that occurs frequently.
- Chest pain, shortness of breath, or fatigue that comes on suddenly.
- Personal history of heart disease, heart attack, or cardiomyopathy — all increase the risk of Sudden Cardiac Arrest.
Conclusion
Sudden Cardiac Arrest is a critical condition that demands quick awareness, early diagnosis, and rapid response to prevent long-term complications. Understanding how Sudden Cardiac Arrest occurs, recognizing symptoms, and knowing when to seek medical help can protect you and your loved ones. With the right medical guidance and timely intervention, many risk factors can be managed effectively. Always stay informed, take preventive heart care seriously, and reach out to a healthcare provider whenever you notice symptoms or risk signs. Prioritizing your heart health today can save a life tomorrow.